The last month has brought notable developments in Queensland and across Australia, particularly with the introduction of the Queensland Digital Licence App and the launch of Australia’s Cyber Security Strategy. In this blog, we will explore these key updates and their impact throughout November.
Queensland’s Digital License App
On November 1st, Queensland followed in the footsteps of New South Wales and South Australia and introduced the Digital License app. Queenslanders can now store identification documents in a digital format which changes how licensed sites and venues manage security and age verification.

(Source: Queensland Government)
One of the primary challenges for security personnel in venues is ensuring patrons are of legal age since physical IDs can be forged or tampered with. Queensland’s Digital Licence overcomes this through:
- Streamlined Verification: The app enables quick scanning of the patron’s ID, making age verification quicker and more reliable
- Enhanced Security: The app’s advanced features make IDs more secure and less prone to tampering, hence, decreasing the likelihood of fraudulent entries
- Reduced Overhead: Digital IDs minimise the risk of any verification errors, ensuring only qualified patrons gain entry to sites.
Operational Implementation
For businesses, the use of the Digital Licence App means operational adjustments may need to be made to combat fraud and ensure compliance:
- Staying up to date on the latest news and updates surrounding the app
- Training staff to recognise and effectively use the Digital Licence App
- Ensuring that the Digital ID presented is from Queensland’s official Digital Licence app
- Confirming that the device used to display the Digital ID is owned by the patron; and
- Understanding the legal framework of Digital IDs to ensure compliance
It is also important to adhere to data protection regulations and management of personal data with care.
Australia’s Pivotal Cyber Security Strategy 2023-2030
Recognising the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and crimes, the Australian Government released a comprehensive Cyber Security Strategy on November 22. This document, which includes detailed initiatives and legislative reforms, aims to build Australia’s national cyber resilience and establish Australia as a global leader in cybersecurity.
Recent high-profile cyber incidents, like the Optus and Medibank data breaches in 2022, underscore the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. The 2021-2022 report from the Australian Cyber Security Centre also highlighted that cyber incidents occurred on average every 7 minutes with over 760,000 cybercrime reports filed, emphasising the urgency of this strategy.

Core Objectives
The strategy’s main goal is to position Australia as a global cybersecurity leader by 2030. This will be implemented in three ‘Horizons.’
Horizon 1 (2023-2025) focuses on strengthening Australia’s cyber foundations, addressing all gaps, and building stronger protection for vulnerable communities. Horizon 2 (2026-2028) will aim to scale cybersecurity across the economy, with the Government investing in the cyber ecosystem and cultivating a diverse cyber workforce. Finally, Horizon 3 (2029-2030) positions Australia at the forefront of global and regional cybersecurity, capable enough to adapt to emerging cyber technologies and threats.
In the process, the Government hopes to build six cyber ‘shields’ with businesses and citizens at its core.
- Strong businesses and citizens: Strengthening cybersecurity for businesses and providing Australians with tools against cyber threats.
- Safe technology: Establishing trust in digital products and protecting sensitive data.
- World-class threat sharing and blocking: Developing a threat intelligence network and enhancing threat-blocking capabilities.
- Protected critical infrastructure: Strengthening security in essential services and infrastructure.
- Sovereign capabilities: Addressing skill gaps and fostering a robust cybersecurity sector.
- Resilient region and global leadership: Enhancing cyber resilience in the APAC region and shaping international cyber norms.
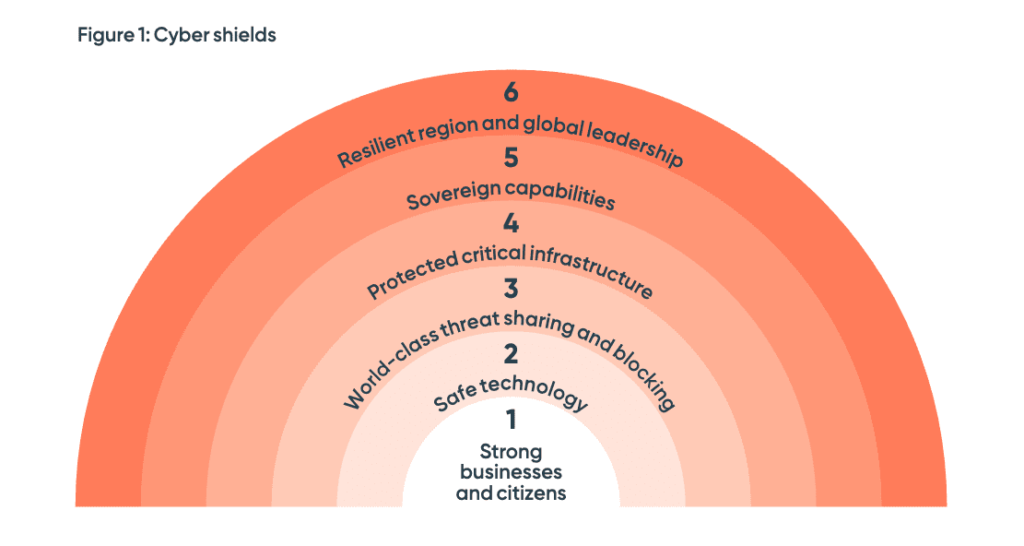
(Source: 2023-2030 Australian Cyber Security Strategy)
Furthermore, the Strategy outlines several legislative reforms and initiatives to be undertaken if we are to strengthen cyber security and resilience.
Ransomware Reporting Obligations
This is designed to enhance government visibility into ransomware threats. This will be a no-fault, no-liability framework for businesses to report ransomwareƒ incidents, aiding in the development of more effective cyber threat management and response strategies.
Data Retention Requirements
The Strategy recommends revising data retention standards, particularly for non-personal data. This revision is aimed at mitigating risks associated with entities that hold large volumes of data for extended periods.
Amendments to the Security of Critical Infrastructure Act (SOCI Act)
Proposed amendments to the SOCI Act seek to increase the Government’s capabilities in cyber security. This would include tougher cyber reporting requirements on telecommunication companies and enhancing the cyber security obligations of entities involved in critical infrastructure.
Cyber Security Standards for Smart Devices
The Strategy introduces a mandatory cyber security standard for Internet of Things (IoT) devices along with a voluntary labelling program for consumer smart devices. This is accompanied by a voluntary code of practice for app stores and app developers to boost cyber security in software development.
Conclusion
The Cyber Security Strategy 2023-2030 demonstrates Australia’s commitment to a secure digital future, balancing technological evolution with robust cybersecurity measures. This calls for partnerships among government, industry experts, and individuals to enhance national cyber resilience.
Our business prides itself in offering advanced security technology and risk management solutions that align with the Government’s new cybersecurity direction. Our background in technology innovation places us at the forefront of supporting these strategic objectives in cybersecurity, particularly in enhancing cyber capabilities for our clients and implementing safer technology practices.
